Everything You Need to Know About the Hebrew Alphabet
Learning the Hebrew language can seem intimidating to some. It’s important not to get overwhelmed, and just start with the basics. The very first thing, when learning Hebrew online or in person, is to familiarize yourself with the Hebrew alphabet.

So, this post will offer a brief guide to the Hebrew alphabet, and what you should know about it if you’re just starting to learn Hebrew as a novice.
Hebrew Alphabet: Introduction
The Hebrew alphabet is comprised of 22 letters and unlike most European languages, the words are not written from left to right but rather right to left. This transition can be a difficult one to make, but soon learners can quickly get the hang of it.
However, as is the case with most Semitic languages, there are certain sounds that can be difficult or rather new to pronounce. These sounds mostly come from the back of the throat. As you familiarize yourself with the Hebrew alphabet, you can practice your pronunciation too.
Another interesting thing to know about the Hebrew language is that verbs can take different forms depending on the gender of the sentence’s subject.
History of Hebrew Alphabet
Much like Modern Hebrew, the Early Hebrew alphabet also contained 22 letters with only consonants represented and was also written from right to left. Between the 6th and 2nd century BCE, the classical alphabet replaced the Aramaic alphabet.
Square Hebrew was then established during the 2nd and 1st century BCE and has since developed into Modern Hebrew. Although it has been largely derived from the Aramaic alphabet, the Early Hebrew script still had a strong influence.
Further Reading: Hebrew Alphabet Origins: How They Began
Characters in the Hebrew Alphabet
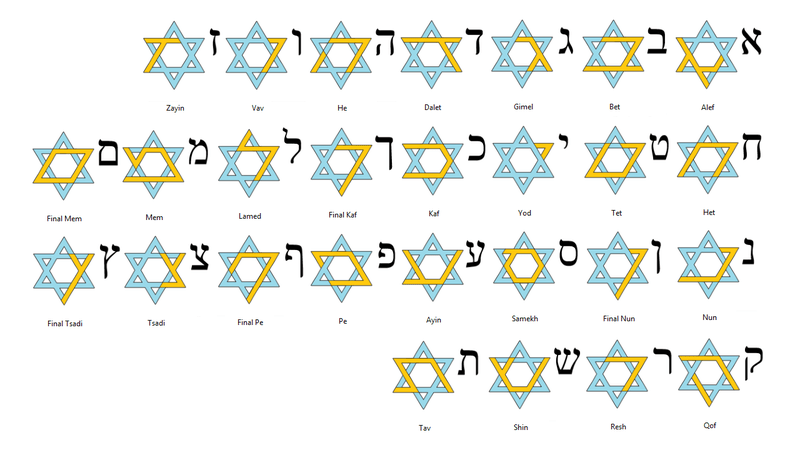
You may be counting more than 22 characters and that’s because five of the letters have a different form when placed at the end of any word.
Interesting Facts About the Hebrew Alphabet
The printed form of the Hebrew alphabet is known as block letters (otiot dfus) and is used for books, newspapers, and street signs. The cursive form (otiot ktav) is used for writing by hand and the letters are rounder than the block letters.
Another interesting fact about the Hebrew alphabet is that all the letters are consonants although four letters can also be used as vowels. The vowels (Nikkud) are a system of vowel signs (small lines and points) that are used to indicate vowels.
However, the use of Hebrew letters in every day, as well as books and newspapers, is done without these vowel signs. Hebrew speakers know how to read the words based on the context and recognition of the words.
A final interesting tidbit is that while letters are written from right to left, the numbers are written and read from left to right. If you want to learn more about the Hebrew language, you can try online Hebrew learning courses from Ulpan-Or.
Ulpan-Or is a leading Hebrew learning institution offering online learning programs, self-study courses, and tons of Hebrew learning materials. Contact now to learn more.



